What is a regulated profession?
A regulated profession is one that has legal guidance, with a formal definition of the rights and duties of professionals in the exercise of their activities (requirements, areas of activity, competencies, etc.).
Generally, these professions are represented by a Class Council, which acts, among other things, to supervise and organize these professionals.
For example, lawyers, doctors, accountants, real estate brokers, architects and others are considered regulated professionals.
Tax regimes currently applied to these professionals
Currently, professionals classified in this category can opt for 3 tax regimes: Simples Nacional, Lucro Presumido or Lucro Real.
For each tax regime there is a specific tax burden. Below is a structured summary. Check it out!

[1] Sub-limit of R$3,600,000.00 created for ISS.
[2] It is worth mentioning that, in order to calculate the tax due for the month, the taxpayer calculates the effective rate (gross revenue accrued in the last 12 months (x) rate provided for in Annex II (-) portion to be deducted (/) gross revenue accrued in the last 12 months). Furthermore, if the ratio between payroll and gross revenue in Simples Nacional is less than 28%, Annex V will apply, which imposes higher taxation, with rates varying between 15.50% and 30.50%, according to the bands described (R Factor).
[3] It is important to note that some services can use the reduced rates, based on the exceptions provided for by law/instruction (for example: Normative Instruction No. 1700 of 2017).
[4] This is levied on the portion of profits that exceeds an annual amount of R$240,000.00 (equivalent to R$20,000.00 per month).
Impact of the Tax Reform on the service sector
The unification of taxes and the simplification of the collection system are positive steps.
In addition, the tax reform seeks to create less distortion in the economic effects of the production chain by adopting the Value Added Tax (VAT) system, i.e. taxpayers will have the full right to use credits and taxation at destination.
The adoption of Value Added Tax (VAT) allows companies to benefit from the right to a tax credit for all the taxes (IBS and CBS) levied in the previous chain, with the right to offset these amounts against the taxes (IBS and CBS) levied on the provision of services.
Complementary Bill No. 68/2024
The first bill to regulate the Tax Reform was approved by the Chamber of Deputies and now goes to the Federal Senate for consideration and presidential sanction.
PLP 68/2024 is responsible for instituting the Tax on Goods and Services – IBS, the Social Contribution on Goods and Services – CBS and the Selective Tax – IS. The basic text approved included an estimated 26.5% cap on the rate of the future Value Added Tax (VAT).
The proposal states that an assessment will be made in 2031 to check whether the sum of the CBS and IBS rates, which will come into full effect in 2033, will result in a figure higher than 26.5%. In the event that the figure is higher than estimated, a new bill will have to be sent by the Executive Branch, in conjunction with the Management Committee, in order to propose a reduction in benefits for sectors or products.
What will change with the approval of the Tax Reform?
Taxation will take place through the application of a maximum rate estimated at 26.5% on company revenue. It is therefore undeniable that the service sector will suffer a real increase in the tax burden.
It is important to note that the approved proposal, through the “Differentiated Taxation Regimes”, provided for a 30% reduction in rates for service providers described as “intellectual, scientific, literary or artistic professions subject to supervision by a professional council”.
The reduction in rates for the provision of services applies to legal entities in which the partners are supervised by a professional council and are directly linked to the company’s objectives. In addition, they cannot have legal entities as partners and the services must be provided directly by the partners.
An obvious change is that the reduction in tax rates is not prevented by the legal nature of the company, the way in which profits are distributed or the union of different professions, as long as each partner works within their professional qualifications.
In addition, some regulated professions related to the provision of services were included in the 60% reduction in tax rates, such as doctors and nurses. Thus, the health sector was one of the main beneficiaries of the basic text of the tax reform regulation.
Since it was possible to observe the 60% reduction in rates for some medical services, such as: surgical, medical clinic, laboratory, dental, among others, in addition to the fact that these services will not be part of the IBS and CBS calculation base for health services.
The reduced rates are considered to be a substantial benefit for the sector and, consequently, for consumers, representing a relief in terms of the tax burden, as well as encouraging the quality and accessibility of the services provided.
Generally speaking, despite the planned reductions, these professionals will be impacted by the possible increase in the tax burden, both due to the limitation and the tax credits related to payroll.
The table below summarizes the main changes brought about by the tax reform compared to the current system:
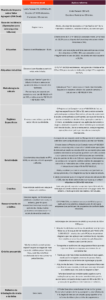
The comparative table above shows the changes that could occur with the Tax Reform in the service sector, but specifically in the regulated professions.
Did you like the content? We hope it has clarified what will change for regulated professions with the Tax Reform.
If you have any questions, click here and talk to our team of experts.








